Definition of "Rubella"
Last modified: less than a minute
It's a disease caused by the rubella virus.
It can cause a maculopapular rash, which means a combination of red and bumpy. It usually fades away after 3 days, so it's a quicky. It can cause swollen lymph nodes. It can also cause flu like symptoms, so high temperatures, sore throat, feeling tired.
Rubella (from Latin "little red", aka German measles, 3 day measles) is a disease caused by the rubella virus. Known as "German" measles because it was first described by German doctors.
Patient information
What is rubella?It's a disease caused by the rubella virus.
Sx
- Disease is often mild, and attacks often pass unnoticed. Minimal systemic upset
- Maculopapular rash, the primary Sx
- Pink or light red, not as bright as measles
- Itchy
- Begins on the face, which spreads to the trunks/limbs, the facial rash usually clearing up as it spreads to other parts of the body
- Usually fades away after 3 days, w/ children recovering more quickly than adults. As it dissapears, there is no stainng or peeling of the skin. However, skin might shed in very small flakes where the rash covered
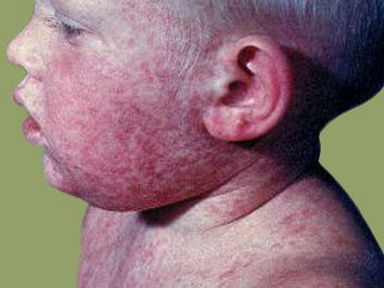
Source: 2014/06/campak-dan-rubella.jpg">Mom-Kid.com
- Swollen lymph nodes are common, and may last a few weeks
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Fatigue
- Transient arthropathy (joint pain) may occur in adults
- Deterioration of the skin are very rare
Patient information
What happens in a disease caused by the measles virus?It can cause a maculopapular rash, which means a combination of red and bumpy. It usually fades away after 3 days, so it's a quicky. It can cause swollen lymph nodes. It can also cause flu like symptoms, so high temperatures, sore throat, feeling tired.
Pathophysiology
- Rubella virus is the pathogenic agent of the disease rubella, and is the cause of congenital rubella syndrome when infection occurs during the 1st weeks of pregnancy. It belongs to the family Togaviridae, whose members commonly have a genome of single-stranded RNA of positive polarity which is enclosed by an icosahedral capsid. The molecular basis for the causation of congenital rubella syndrome are not yet completely clear, but in vitro studies with cell lines showed that rubella virus has an apoptic effect on certain cell types. There is evidence for a p53-dependent mechanism
- Acquired rubella is transmitted via airborne droplet emision from the upper respiratory tract of active cases. The virus may also be present in urine, feces, and on the skin
- Only humans are infected, and reservoirs. Insects do not spread the disease
- Disease has incubation period (i.e. time between exposure to pathogen, to when Sx first appear) of 2 weeks
- Pt's are infectious during the week before, and after the appearance of the rash. Babies born with CSR however, may be infectious for more than 1 year. CRS is thus a significant reservoir, to other infants, and importantly, pregnant women
Dx
- Verify immunity, by:
- Finding the virus in blood, throat, or urine
- Testing blood for IgM antibodies, in Pt's recently infected, which can persist for over 1 year
Tx
- Prevention, w/:
- Rubella vaccine, with a single dose is >95% effective. It is often given as the MMR vaccine, w/ measles and mumps
- In mothers, offered to all susceptible non-pregnant women of childbearing age. Note however, that because of possible teratogenicity, MMR vaccine is NOT recommended during pregnancy, but should be vaccinated ASAP in the postpartum period
- In the newborn, MMR is recommended 1st at 12-18mo, and a 2nd dose at 36 months
- Screening, of all women of childbearing age at their 1st preconception counselling visit, via Hx of vaccination, or by serology
- Rubella vaccine, with a single dose is >95% effective. It is often given as the MMR vaccine, w/ measles and mumps
- Sx relief, as there is no specific Tx once infected. Newborns affected involve:
- Surgery → congenital heart defects, cataracts
- Low vision devices → macular degeneration
- Counselling and monitoring
Prognosis
- Usually mild, self limiting, and often asymptomatic
- Except for CRS, the virus is rapidly eliminated in most Pt's
- Once recovered, Pt's are immune to future infections
- Prognosis of kids born w/ CRS is poor
Complications
- Bleeding problems
- Testicular swelling
- Neuritis (inflammation of nerves)
- Infection of a mother during pregnancy, is serious; if the mother is infected <20 weeks gestation (particularly trimester 1), it can cause congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) or miscarriage (20%), as the infection passes through the placenta, causing problems with the eyes (e.g. cataracts, blindness), ears (e.g. deafness), heart (e.g. patent ductus arteriosus), and brain. It may also cause prematurity, low birth weight, neonatal thrombocytopenia, anemia, and hepatitis. CRS is the main reason the rubella vaccine was developed
Epidemiology
- Common childhood infection, in many areas of the world
- Each year, 100k cases of CRS occur
- Rate of disease has decreased due to vaccination, w/ WHO declaring in 2015 America was free of rubella. There are ongoing efforts to eliminate the disease globally
- The population vaccination rate of MMR is <80%, so women might make it to childbearing age w/o developing immunity
Many others who contract rubella within trimester 1 have a miscarriage or stillborn - Notifiable disease
See also
- Measles (do not confuse rubella with "rubeola"

- Scarlet fever
- Dukes' disease
- Fifth disease
- Roseola infantum
- TORCH complex (rubella is a constituent)
- Congenital rubella syndrome
Synonyms:
3 day measles
German measles
Rubella immune
Rubella non immune
Rubella virus
Three day measles
Find a practitioner
Practitioner count: 0
Sponsor a disease. And see how your proceeds help.
$1
Express interest
$10
Write text
$40
Write FAQ
$100
Snap photos
$400
Record audio
$1k
Produce video
$4k
Interview experts